Yet, some plastics are hard to mechanically recycle and may end up as waste. ExxonMobil is deploying advanced recycling technology and collaborating to collect plastic waste so that more of the plastics we rely on every day can be recycled, instead of ending up in landfill, incineration or the environment.
Why does advanced recycling matter?
The OECD estimates that only 9% of plastics are recycled globally, so what could help lift these numbers?
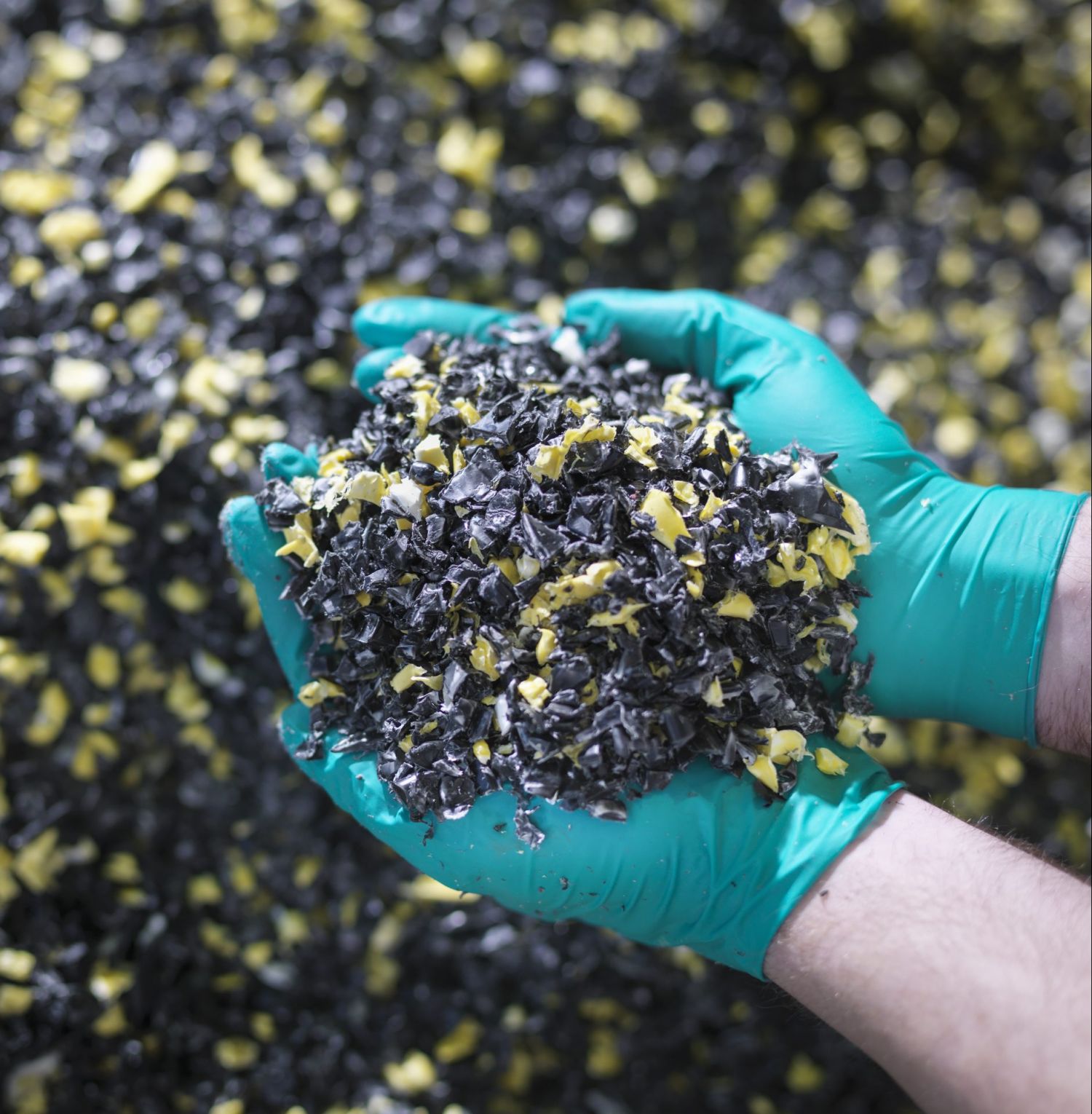
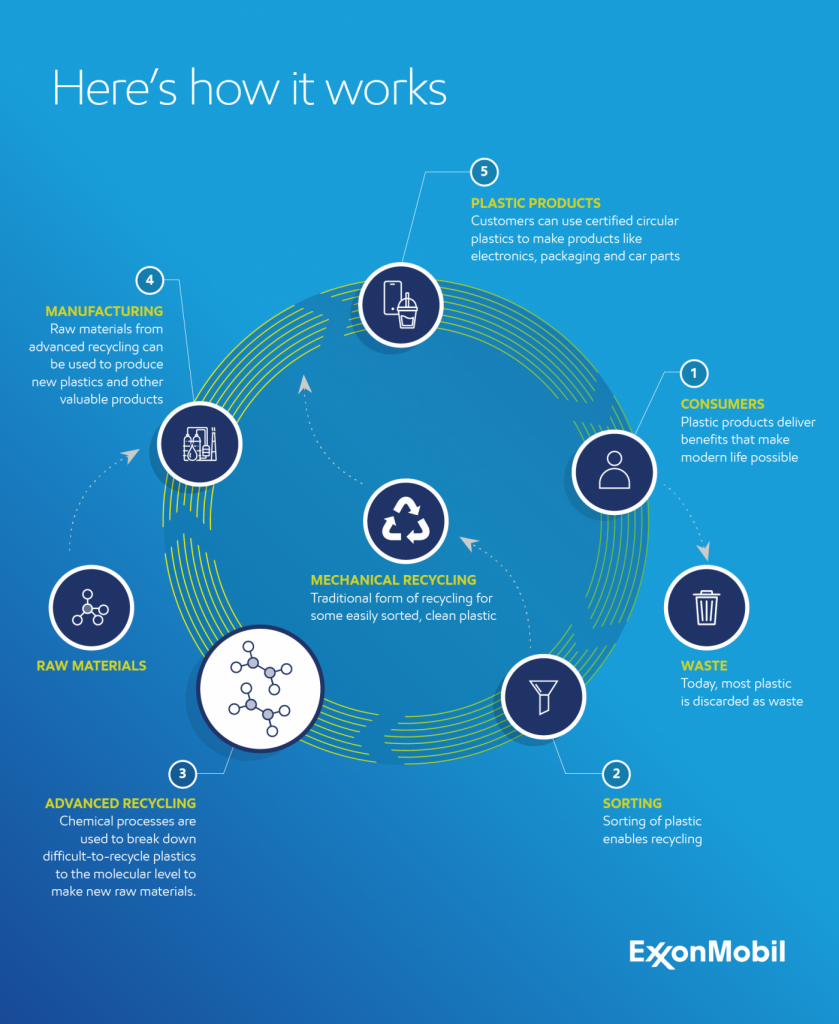
Advanced recycling, also known as chemical recycling, can help boost this figure. It works by breaking down hard-to-recycle plastics into molecules that can be repurposed to make new everyday products.
“By deploying advanced recycling, ExxonMobil is making it possible for a far broader range of plastic waste to be recycled. This puts us one step closer to a world where society can better capture the value of plastic waste,” says Kwee-Lin Chan, ExxonMobil’s Advanced Recycling and Sustainability Market Manager for Asia Pacific.
How does advanced recycling work?
Once sorted and shredded, plastic waste is heated and chemical processes then break it down into molecular building blocks. These building blocks are then combined with other materials that can be made into a variety of products, including new plastics with the same quality and performance as virgin plastics.
Recycling and repurposing these plastics can create a circular economy in which plastics are made into new products instead of ending up in landfill, incineration or, worse, the environment.
Because it is difficult to track the molecules that originated from the plastic waste, industry uses an internationally recognized third-party certification system called ISCC PLUS and follows its mass balance attribution approach to certify the circularity of the plastics that industry sells based on the amount of plastic waste processed. This approach is analogous to those used by the renewable electricity and sustainable farming industries. The certified-circular plastics we sell are identical in quality and performance as our existing products, enabling them for use in food and medical applications that carry strict quality regulations, helping to meet growing customer demand.
Advanced recycling’s difference
![]()
Now and into the future
In December 2022, ExxonMobil started up a large-scale facility in Baytown – one of North America’s largest advanced plastic waste recycling facilities, which has processed more than 9,200 metric tons of plastic waste since pilot operations began at the site in 2021 through June 2023. The facility has the capacity to process up to 40,000 metric tons of plastic waste per year.
Through this advanced recycling operation in Baytown, ExxonMobil is making sales of ISCC PLUS certified-circular plastics in the U.S., Canada, Mexico, Europe and Asia Pacific, helping to meet customers’ goals around the world for circularity. This includes sales in Asia Pacific to Scientex and Amcor for use in flexible packaging. In India, ExxonMobil has made its first commercial sale to the country’s largest multinational flexible packaging and solutions company UFlex Limited, which will use these certified-circular plastics to produce high-performance food-grade packaging.
Leveraging existing assets and the technology used in Baytown, ExxonMobil plans to increase annual advanced recycling capacity to 500,000 metric tons by year-end 2026 across multiple sites globally.
Our work in Asia Pacific
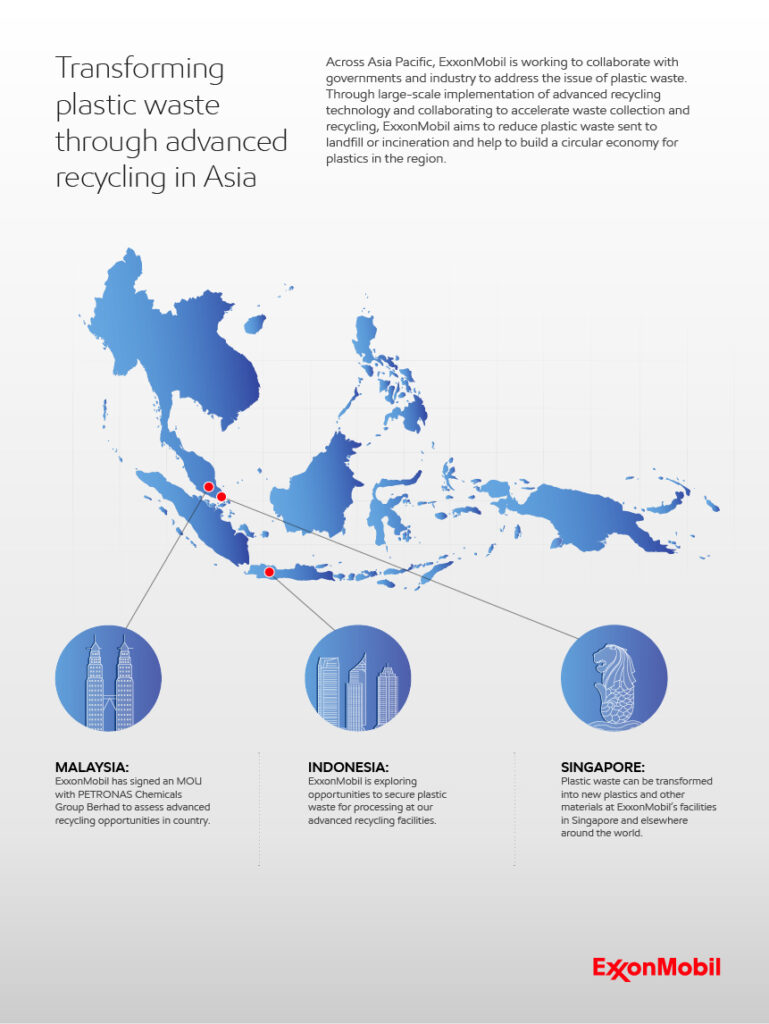
In Asia Pacific, ExxonMobil is working to collaborate with governments, industry and technology providers to accelerate waste collection and sortation and assess the potential for large-scale advanced recycling facilities across the region.
In September 2022, ExxonMobil and PETRONAS Chemicals Group Berhad signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to assess large-scale advanced plastic recycling opportunities in Malaysia.
In Indonesia, ExxonMobil is exploring opportunities to secure plastic waste for processing at our advanced recycling facilities.
Our aim is to address plastic waste that may end up in landfill or incineration by sending the plastic instead to an advanced recycling facility. There, the plastic waste can be transformed at ExxonMobil’s facilities in Singapore, and elsewhere around the world, into raw materials used to make virgin-quality plastic and other valuable new products.
ExxonMobil is also exploring other advanced recycling opportunities across Asia Pacific, helping to accelerate a circular economy for plastics in the region.